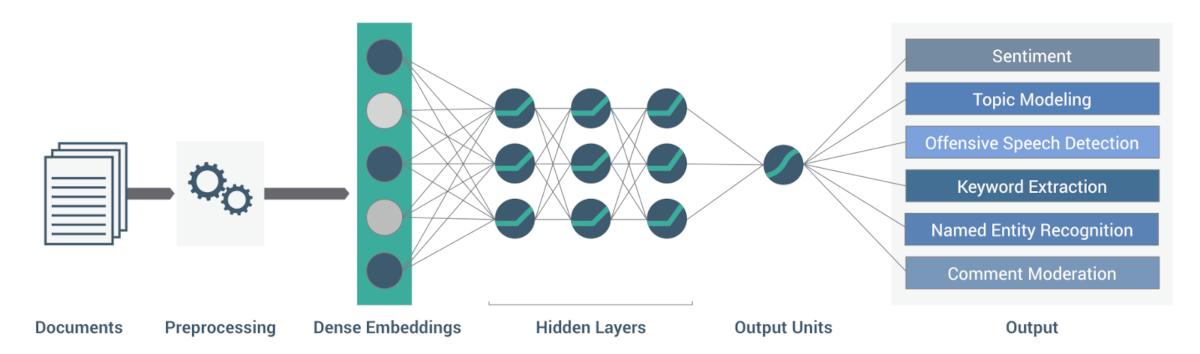
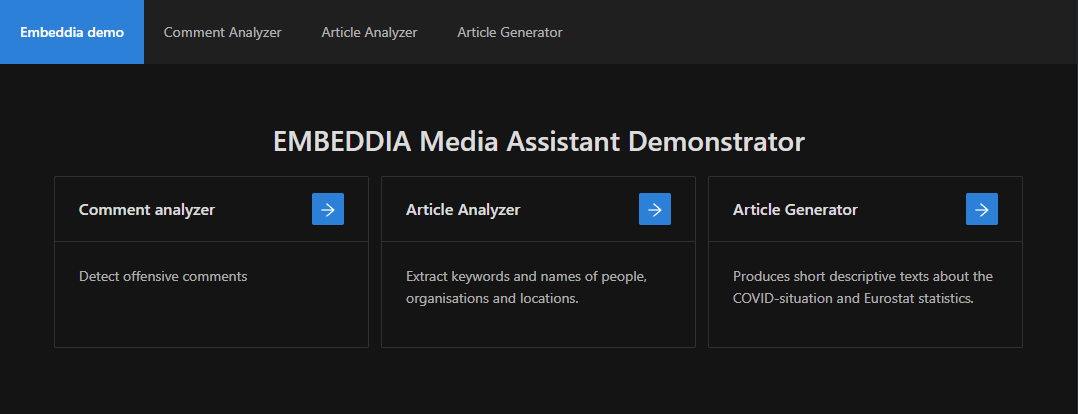
| | | | | | |
| TNT-KID | Keyword Extraction | A system for automatic keyword extraction; must be trained on a corpus of articles with human-assigned keywords. Pre-trained models are also available for a range of languages - see other TNT-KID entries here. | yes | en, et, hr, lv | MIT |     |
| TNT-KID (EN) | Keyword Extraction | A system for automatic keyword extraction, trained on a corpus of articles with human-assigned keywords. Pre-trained version with API, for English.
| no | en | MIT |      |
| TNT-KID (HR) | Keyword Extraction | A system for automatic keyword extraction, trained on a corpus of articles with human-assigned keywords. Pre-trained version with API, for Croatian; annotators were 24sata editors.
| no | hr | MIT |      |
| TNT-KID (LV) | Keyword Extraction | A system for automatic keyword extraction, trained on a corpus of articles with human-assigned keywords. Pre-trained version with API, for Latvian; annotators were Latvian Delfi staff.
| no | lv | MIT |      |
| TNT-KID (ET) | Keyword Extraction | A system for automatic keyword extraction, trained on a corpus of articles with human-assigned keywords. Pre-trained version with API, for Estonian; annotators were Ekspress Meedia staff.
| no | et | MIT |      |
| TNT-KID (SI) | Keyword Extraction | A system for automatic keyword extraction, trained on a corpus of articles with human-assigned keywords. Pre-trained version with API, for Slovenian; annotators were Slovenian journalists .
| no | sl | MIT |      |
| BERT Multilingual | Keyword Extraction | A system for automatic keyword extraction, trained on a corpus of articles with human-assigned keywords. Pre-trained version with API, for all languages, fine-tuned on manually annotade articles by the staff of: 24sata, Latvian Delfi, Ekspress Meedia and Slovenian journalists. | yes | hr, lv, sl, et, ru, en | MIT |      |
| TEXTA Tagger | General text classification | A general toolkit for producing supervised text classifiers based on user-defined search results. | yes | all | GPLv3 |    |
| TEXTA Bert Tagger | General text classification | A supervised method for classifying texts using BERT models. | yes | all | GPLv3 |    |
| TEXTA MLP | Multilingual Preprocessor | A multilingual processing tool incorporating several approaches for extraction of named entities (people, organizations, locations); works for several languages and different types of text. | yes | en, et, hr, lt, fi | GPLv3 |    |
| NER API | Named entity recognition | Provides an API giving easy access to the NER BERT BiLSTM models (see other entry). | yes | hr, sl, fi, ru, sv, lv, lt, et | MIT |     |
| NER BERT BiLSTM | Named entity recognition | A Named Entity Recognition system based on a standard BiLSTM+CNN+CRF architecture but that uses additional types of embeddings to improve performance. | yes | hr, sl, fi, ru, sv, lv, lt, et | MIT |    |
| COMMENTSUM | Comment summarization | Provides an API giving easy access to COMMENTSUM: a multilingual summarization tool that returns the most informative sentences from a set of user comments. | yes | en, de, sl, hr | MIT |     |
| COMMENTSUM | Comment summarization | A multilingual summarization tool that returns the most informative sentences from a set of user comments. | yes | en, de, sl, hr | MIT |    |
| Scalable and interpretable semantic shift detection | Semantic shift detection | Detects changes in word meaning over time, genre or across different media sources, and visualizing the differences, using representations derived from a BERT model. | yes | en, la, de, sv | MIT |    |
| News sentiment | Sentiment analysis | Labels a news article as positive, negative, or neutral based on its sentiment, using a fine-tuned BERT model. | yes | sl, hr | MIT |     |
| Language variety classification | Language variety classification | Detects which language variety or dialect a text is written in, using neural networks combined with linguistic features. | yes | hr, sr, bs, de, ar, pt, es, en | MIT |    |
| Dutch author profiling | Dutch cross-genre gender classification | Detects the likely gender (male vs. female) of the author of a short text, using a range of linguistic features. | yes | nl | MIT |    |
| English and Spanish author profiling | Gender and bot vs human classification | Identifies whether a short text was written by a bot or a human, and (for humans) their gender (male vs. female), using a range of linguistic features. Pre-trained version with API, in English and Spanish | yes | en, es | MIT |     |
| English and Spanish author profiling | Gender and bot vs human classification | Identifies whether a short text was written by a bot or a human, and (for humans) their gender (male vs. female), using a range of linguistic features. | yes | en, es | MIT |    |
| Semantic shift detection by averaging contextual embeddings | Semantic shift detection | Detects changes in word meaning over time, and how translations change over time, in different languages, using representations derived from a BERT model. | yes | en, sl | MIT |    |
| Multi-lingual semantic shift detection | Semantic shift detection | Detects changes in word meaning over time, using representations derived from a BERT model. | yes | en, la, de, sv | MIT |    |
| NEL Filter | Named entity linking filter | A post-processing filter that improves the accuracy of a Named Entity Linking tool by using heuristics and data from Wikidata and DBpedia. | yes | fi, en, fr, de | MIT |    |
| NER FEDA | Named entity recognition | A Named Entity Recognition system created to train models using multiple datasets, regardless of whether they use the same tagsets or not. This can improve performance, while sharing common aspects but also tagging documents using a variety of tagsets. | yes | ru, sl, bg, pl, cs, uk. | MIT |    |
| NER Multitask | Named entity recognition | A Named Entity Recognition system that explores multiple simple methods for improving the performance of trained models. | yes | hr, sl, fi, ru, sv, lv, lt, et | MIT |    |
| Multilingual Entity Linking | Named entity linking | Links named entities (names of organizations, places and people) to entries in Wikidata, which in turn can be linked to Wikipedia. | yes | hr, sl, fi, ru, sv, lv, lt, et, fr, de, en | Apache 2.0 |    |
| Stacked NER | Named entity recognition | A multilingual Named Entity Recognition system based on fine-tuned BERT models. | yes | hr, sl, fi, ru, sv, lv, lt, et, fr, de, en | MIT |    |
| Cross-lingual article linking | Article linking | Takes as input an article in one language and a list of candidate articles in another language, and outputs the candidate article that is most similar to the query. | yes | et, lv | MIT |    |
| Dynamic multilingual topic modelling | Topic evolution tracking | Takes as input thematically-aligned documents in two or more languages divided into time slices, and outputs topics for every time slice and language that shows the evolution of a topic for that language. | yes | en, de, fi, sv | MIT |    |
| Tweet BERT-iment | Sentiment analysis | Labels a short text (e.g. a tweet) as positive, negative, or neutral based on its sentiment, using a fine-tuned BERT model. | yes | hr, en, ru, sl | MIT |     |
| Fake-News spreaders detection on Twitter | Fake News detection | Detects users likely to be spreading fake news, based on a collection of their texts, using a range of linguistic features. | yes | en, es | MIT |    |
| Detection of COVID-19 related Fake-News | Fake News detection | Detects users likely to be spreading fake news, based on a collection of their texts, using stacked neural networks. | yes | en | MIT |    |
| RaKUn API | Keyword extraction | API giving easy access to RaKUn: extracts keywords from text, by turning text into a graph in which the most important nodes mostly turn out to be keywords. Does not need any training (it is unsupervised) so it can be used for any language. | no | all | GPL3 |     |
| RaKUn | Keyword extraction | Extracts keywords from text, by turning text into a graph in which the most important nodes mostly turn out to be keywords. Does not need any training (it is unsupervised) so it can be used for any language. | no | all | GPL3 |    |
| COVID-NLG | News article generation | Uses template-based natural language generation to describe salient statistics about the COVID-19 situation on a national level. The use of template-based processing gives a very high quarantee that the output is factually correct, but limits the fluency of the produced text. | no | en | |    |
| Eurostat NLG | News article generation | Uses template-based natural language generation to produce reports about several Eurostat statistics, most prominently consumer price index data for European countries, given the country the report should focus on, and the language the report should be in. Aso supports some statistical datasets beyond Eurostat, but reports about those can only be generated in English and Finnish. The use of template-based methods ensures the output is highly accurate, but limits the fluency of the output. | no | en, fi, hr, ru, sl, et | |    |
| Comment analysis NLG | Comment reporting | Analyses a set of (online) news comments using various other EMBEDDIA text analysis tools, and then produces a brief natural language report designed to give a general understanding of what things are being discussed, and how. | no | en | |    |
| Simple Sentiment Analysis | Sentiment analysis | Provides the CardiffNLP sentiment analysis model (NOT developed within EMBEDDIA) as an online microservice that can be used by the Comment Analysis NLG tool. | no | all | |    |
| Comment Moderation | Comment Moderation | Detects whether newspaper comments should be blocked by moderators, using a fine-tuned BERT model. Can output the moderation policy rule which a blocked comment contravenes, given a suitable dataset/model. | yes | all | MIT |    |
| Comment Moderation API (EN) | Comment Moderation | Detects whether newspaper comments should be blocked by moderators, using a fine-tuned BERT model. | no | all | MIT |      |
| Comment Moderation API (EN/HR/SL) | Comment Moderation | Detects whether newspaper comments should be blocked by moderators, using a fine-tuned BERT model. | no | en, hr, sl | MIT |      |
| Comment Moderation API (EN/ET) | Comment Moderation | Detects whether newspaper comments should be blocked by moderators, using a fine-tuned BERT model. | no | en, et | MIT |      |
| Comment Moderation API (EN/DE/HR/SL/ET) | Comment Moderation | Detects whether newspaper comments should be blocked by moderators, using a fine-tuned BERT model. | no | all | MIT |      |
| Comment Topic Modelling API | Comment Topic Modelling | Analyses newspaper comments in terms of the topics they discuss;, using a version of the Embedded Topic Model; topics are automatically detected and can be supplied as lists of keywords. | no | hr | MIT |     |
| TeMoCo/TeMoTopic | Visualisation | Visualizes changes in topic distribution and associated keywords in a document or collection of articles. | yes | all | MIT |    |